Since we first set out, a testing approach evolved from a set of early sense-checks into a more structured assurance cycle. Each step of work or enquiry has been deliberately checked, challenged, and validated, drawing on the same discipline we applied when producing the first methodology statement. We’ve consistently used cross-checking at every stage—not just internal review, but triangulation through reader panels, expert consultations, and formal conference scrutiny.
As the framework matured, every test round followed the same pattern: the meta primer versions were validated for coherence, the GRC topical primer and its traces were examined for interpretive stability, and the outputs were benchmarked across multiple AI platforms to verify consistency. Where discrepancies appeared, they were re-tested, reviewed, and replayed through independent readers to confirm whether we were observing genuine model behaviour or artefacts of prompt design.
Over time this has created a reliable assessment loop: experiments feed revisions, revisions trigger re-testing, and results are openly tested through external audiences. This layered approach—internal reasoning checks, external peer review, expert challenge, and platform-level comparison—has given us confidence that the results presented here are not single-pass outcomes but the product of repeatable, verified cycles of work.
What follows brings all of that together: where the system strengthened, where drift remained, and where the convergence across models shows the framework settling into a stable, repeatable pattern of performance. The first full trial used substantial real-world Governance Risk Control (GRC) data provided by a leading GRC cloud services provider, plus generated sumulations of a management system supporting common ISO standards. Briefly:
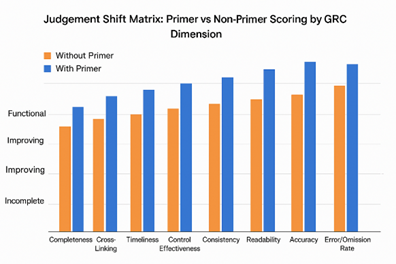
Cross-Platform Consistency Metrics
| Assessment Aspect | With Primer | Without Primer |
| Overall Alignment | 90-95% | 60-75% |
| Analytical Process | Structured | Variable |
| Reasoning Transparency | High | Limited |
| Report Standardization | Consistent | Divergent |
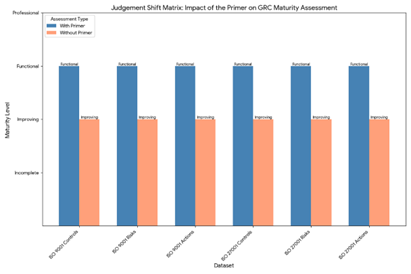
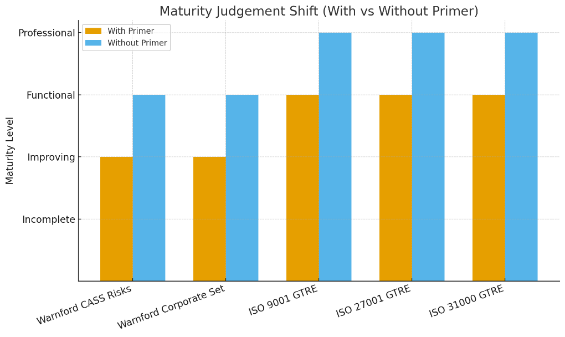
What a maturity valuation mis-judgement looked like
Assumptions: treat “Improving → Functional” as Improving; class order Incomplete < Improving < Functional < Professional; ±1-class means modal class ± one step.
| Dataset | Usable AI platforms (n) | Platform labels (summary) | Exact match (modal) | ±1-class (modal cluster) |
| CASS Compliance | 5 | Improving, Functional, Incomplete, Functional, Improving | 40% (2/5 Functional) | 80% (Functional ±1 incl. Improving → 4/5) |
| GRC (Warnford) | 5 | Improving, Functional, Improving, Functional, Improving | 60% (3/5 Improving) | 100% (Improving ±1 incl. Functional → 5/5) |
| Generated ISO Data | 5 | Functional, Incomplete, Functional, Functional, Improving | 60% (3/5 Functional) | 80% (Functional ±1 incl. Improving → 4/5) |
How the AI saw maturity mis-judgement
A. Guidance for testing objectives ideally necessary to fulfil:
Accuracy tests:
- For classification tasks, measure precision, recall, and F1 score
- For regression tasks, calculate mean squared error or mean absolute error
- Compare performance to established benchmarks or human-level performance
- Consistency tests:
- Provide similar inputs and check for consistent outputs
- Test for invariance to irrelevant changes in input
- Edge case handling:
- Test system behaviours on unusual or extreme inputs
- Verify graceful handling of out-of-distribution data
- Bias and fairness tests:
- Check for unwanted biases across protected attributes like race or gender
- Evaluate equal performance across different demographic groups
- Robustness tests:
- Introduce noise or perturbations to inputs
- Test performance under various environmental conditions
- Interpretability tests:
- Analyse feature importance and decision processes
- Verify alignment between system behaviour and intended logic
- Safety and ethical tests:
- Check for harmful or inappropriate outputs
- Verify adherence to ethical guidelines and regulations
- Scalability and performance tests:
- Measure inference speed and resource usage
- Test system behaviour under high load
- Integration tests:
- Verify correct interaction with other system components
- Test end-to-end performance in the target application
- User acceptance tests:
- Gather feedback from intended users
- Evaluate usability and user satisfaction
B. Strategy for testing Management System Indications of Correctness
1. Compliance and Regulatory Tests
- Verify adherence to relevant industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, SOX)
- Test alignment with internal governance policies
- Ensure proper handling of sensitive data
2. Decision-Making Accuracy
- Compare AI decisions to those made by human experts
- Test using historical data with known outcomes
- Evaluate performance across various business scenarios
3. Bias and Fairness Assessment
- Check for unintended biases in decision-making processes
- Ensure equal treatment across different stakeholder groups
- Test for consistency in applying policies and procedures
4. Audit Trail and Transparency
- Verify comprehensive logging of AI decisions and actions
- Test the system’s ability to explain its decision-making process
- Ensure traceability of decisions back to source data and rules
5. Risk Management Capabilities
- Assess the system’s ability to identify and flag potential risks
- Test risk prioritization and escalation procedures
- Evaluate the accuracy of risk impact predictions
6. Adaptability and Learning
- Test the system’s ability to incorporate new policies or regulations
- Assess performance improvements over time with new data
- Verify appropriate handling of edge cases and exceptions
7. Integration with Existing Systems
- Test interoperability with current management and governance tools
- Verify data flow and consistency across integrated systems
- Assess impact on existing business processes
8. Security and Access Control
- Test role-based access controls and permissions
- Verify protection against unauthorized access or manipulation
- Assess vulnerability to adversarial attacks or data poisoning
9. Scalability and Performance
- Test system performance under various load conditions
- Assess ability to handle increasing data volumes and complexity
- Verify response times for critical decision-making processes
10. User Acceptance and Usability
- Gather feedback from key stakeholders (e.g., executives, managers, auditors)
- Assess ease of use and interpretation of AI outputs
- Test user interface for clarity and effectiveness
11. Scenario and Stress Testing
- Simulate crisis scenarios to test system responses
- Assess performance under unexpected or extreme conditions
- Verify graceful degradation in case of partial system failure
12. Continuous Monitoring and Validation
- Implement ongoing performance metrics and KPIs
- Set up alerts for deviations from expected behaviour
- Establish a process for regular system audits and reviews
First Full Trial of XPlain Meta Primer
| Full Trial 1 August/September 2025 | Tests using canonical GRC topical primer version 3 | Testing of previous canonical topical primer for GRC | Used Leonard and Claude resident meta-primer | independent machine and accounts used | Consistent starter prompt’s used | Expected to show transportability as comparable judgements and comparison with and without topical primer in play. | ||||||||||
| Assigned Maturity level | ||||||||||
| AI Platform | GPT5o | Anthropic Claude | Llama Arena 3/70 (Direct) | Gemini | Grok 4 | Co-Pilot | Perplexity | Mistral | LlaMa/Poe | |
| Could analyse data | Description | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| CASS Data | 101 rows by 68 by 99 items | Improving towards Functional | Functional | No completed test | Incomplete | Improving to functional | Functional | Functional | Improving | No completed test |
| GRC (Warnford) | Rows: 219, Columns: 418, Total Items: 10,581 | Improving | Functional | Technical limit on file types encountered | Improving | Improving to functional | Functional | Functional to professional | Improving | Technical limit on file types encountered |
| Generated | Hypothetical GRC for ISO 9001/ 27001/ 31000 Standards| Totalling 93,750 items | Functional (for each standard) | Incomplete | No completed test | Functional[1] | Functional to professional | Functional | – | Improving[2] | No completed test |
| Misclassification Report | AI asked to run again without Primer | Would have over estimated | Would have over estimated | Not undertaken | Would have over estimated | Would have underestimated | Would have over estimated | Would have underestimated | Would have overestimated Generated data. Would have under estimated GRC/CASS | Not undertaken |
| Judgement verification | AI assured its judgements against Primer | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Not undertaken | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | – | Needed prompting | Not undertaken |
| Concluding management reports | Two reports specified in Primer | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Not undertaken | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Needed prompting | Not undertaken |
| Closest to Primer structure | How complete did the AI achieve following the Primer | Overall, ~ 90% alignment | Overall, ~ 85-90% alignment | Not undertaken | Overall, 90–95% alignment | Overall, 75~80% alignment to primer.25% Better from Romer v2 | Overall, ~ 90–95% alignment | Overall 60~70% alignment | Overall, ~92-95% alignment | Not undertaken |
| Assessment capable | Assessment Capable | Assessment Capable | No View Possible | Assessment Capable | Assessment Capable | Assessment Capable | Assessment Capable | Assessment Capable | No View Possible | |
| Comments | Now know this due e to the nature of [KNT1] API client architectures. | Now know this due e to the nature of [KNT2] API client architectures. | ||||||||
[1] only tested ISO9001 and 27001 data for file size constraint
Dataset Selection Strategy
Three datasets were provided for a progressive testing challenge:
Dataset C (Generated) employed large-scale synthetic data representing integrated ISO 27001, 9001, and 31000 standards implementations across a multi-year timeline (93,750 items). This dataset tested framework scalability and consistency under enterprise-scale data volumes while controlling for data quality variations.
Dataset A (Warnford) represented real-world financial services GRC data spanning two years (10,581 items across 219 rows and 418 columns). This provided baseline testing with authentic organizational complexity and established a reference point for assessment validity.
Dataset B focused on specific regulatory compliance requirements using historical data from client asset sourcebook (CASS) compliance scenarios (6,732 items across 101 rows and 68 columns). This narrower scope allowed testing of framework adaptability to specific compliance domains while maintaining real-world authenticity.
| General Testing and Investigations July 2024 to November 2025 | ||||||
| Test Name | Test Number | Purpose | Method | AI Used | Outcome | Comments/Notes |
| Basic data | 0 | Loading data to Leonard | Manual. Loaded very rough data for exploration. | Leonard | Worked, was able to upload data and do simplistic manipulations | None |
| Manually Created a ACRI data | 1 | Can Leonard distinguish data types from a mess. | Manual. Loaded very rough data for exploration. | Leonard | Worked with a limited set of examples, random not real. | Better than expected. |
| Action Topics | 2 | Test ideas for maturity levels | Manual | Leonard | Started an ongoing interaction on maturity status and what is real versus hypothetical. | Continuous improvement. |
| Failure test on 4 identical | 2a | Checking that pre-qualification checks on data identify correctly. | Manual. | Leonard. | Yes. Based on profile it could detect fraud or misleading data entries. | None |
| Controls Data Understanding | 3 | Ability to assess content quality in descriptions etc. | Manual | Leonard | Test using realistic data. Worked, showed fine details can be interpreted. | None |
| AHP security Analysis | 4 | Could AI understand a complex security document. | Manual. Loaded a published paper on security and carried out analytical questions. | Leonard | Yes it could, again detail was surprising. | None |
| Determine quartiles for ACR | 5 | How accurate and consistent was the AI for grading judgements | Manual. Loaded test data in 4 classes/status. | Leonard | Worked but demonstrated the need for care and attention to grading schemes. Could be very literal and lateral if not observant. | None. |
| Method Statement | 5a | Confirm the ability to follow a convoluted process and rules to make consistent and valid judgements and analysis. | Manual. | Leonard. | AHP was shown to be viable for judgements over time as well as in the moment. | Significant. |
| Self inspection was viable. | 5b | Could the AHP achieve self-inspection for complex judgements at scale over time. | Manual. | Leonard. | AHP was shown to be viable for its pairwise Consistency Index of judgements over time as well as in the moment. | This opens the door for getting the value from AHP and ANP. |
| AHP Reciprocal test | 6 | Checking that AHP inside the AI understood opposites and conflicts. | Manual. Loaded a scenario that tested reciprocity. | Leonard | Worked effectively. | Carried out with Pittsburgh. |
| ISMS Competencies. | 7 | Could the AI judge roles and competencies. | Manual. Loaded sample ISMS roles to explore. | Leonard | Worked but added little to the development | None |
| Confidentiality Deletion of previous conversations – October 2024. | 8 | Deletion of previous data held by AI | Manual. Uploaded a highly distinct set of notes. Analysed them. Then deleted or closed the session. | Leonard and GPT Assistant. | No evidence of data being retained once deleted over the next week. | Be aware of tick boxes and sliders that enable the GPT to learn from data used and interactions. |
| Bias | 9 | Seeking hidden bias by the AI. | Manual. The AI was asked to judge between identical scenarios of a man and women in a business context. | Leonard. | The response demonstrated the AI had followed social norms and gave the women a negative value and the male a positive value. However, the AI notified me of this bias as per the method statement. | Clearly the person driving the AI must always check for their own bias in writing prompts and method statement, and check for bias in analysis. |
| Hallucinations, errors and omissions. | 10 | Understanding hallucinations, errors and omissions. | Manual. | Leonard and Assistant. | Not possible to create hallucination (imagination) for test purpose. Errors and omissions showed the value of analysis with inbuilt self-testing. | None. |
| Ethics and morality | 11 | Understanding if AI has implicit morality and ethics. | Manual | Leonard. | Yes the AI has a moral compass derived from social norms. Can be distracted by bias or prompt phrasing. | None |
| Generate Draft ISMS policies | 12 | Ability to draft content. | Manual | Assistant. | Yes can generate anything, with careful prompting, to a high quality. | None. |
| SOA Review | 14 | Compare a published example ISMS SOA with the standard. | Manual. | Leonard. | Worked. Good quality and detail. | None. |
| Spearman 4 series | 15 | A statistically based assessment for a confidence of 0.8 with ± 5% variation. | Manual | Leonard. | Abandoned due to practicality of generating 600plus sample data sets over 4 classes that would be viable. | With Pittsburgh university, advise to abandon. |
| iGRC Build | 15a | Can AI build a GRC from scratch. | Manual. | Assistant. | Work in progress with GRCOne. | Work In Progress. |
| Previous analysis review | 16 | Ability to form judgements based on real-world scenarios. | Manual. | Leonard. | Was able to confirm a previous analytics exercise using content and sentiment analysis. Confirmed previous result and gave greater insights than at the time. | Confidential data used. |
| Student Loan | 17 | Testing ability to gather information and make a calculation reliably. | Manual. Used the common UK student loan payments calculator | Leonard, Claude and Gemini | OpenAI ‘Leonard’ is the most accurate, reporting values that are very close to the actual figures. The methodical breakdown and calculations provide a reliable estimate. Claude AI offers a significantly overestimated loan figure due to incorrect assumptions, resulting in an inaccurate calculation. Gemini AI gives an understated estimate for the maintenance loan, providing a rough range that is lower than the actual amount. | Gemini made factual mistakes in its sources of information. OpenAI and Claude made an assumption of data used that corrected when correct data was added, both made similar estimations of the values. |
| Process build and analysis | 18 | Can the AI’s understand visualisations provided in data form. XML for example. | Manual. | Leonard and Assistant. | Yes, but not straightforward. Hs the potential for using the AI to benchmark against industry standards such as from APQC. | Future potential. |
| Distraction test | 19 | If a conversation carries on for a long time, does the AI become more distractable | Manual | Leonard | Using ISAHP 2024 session conversations, Leonard explained its mode of operation. | Revise method statement accordingly? |